[자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편] 07강. 고급 매핑
07강. 고급 매핑
1. 상속관계 매핑
상속관계 매핑
- 상속관계 매핑 : 객체의 상속과 구조와 DB의 슈퍼타입 서브타입 관계를 매핑
- 슈퍼타입 서브타입 관계라는 모델링 기법이 객체 상속과 유사 (관계형 DB는 상속 관계 없음)
-
슈퍼타입 서브타입 논리 모델을 실제 물리 모델로 구현하는 방법 (3가지)
전략 상세 Annotation 조인 전략 각각 테이블로 변환 @Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.JOINED)단일 테이블 전략 통합 테이블로 변환 (JPA 기본값) @Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)구현 클래스마다 테이블 전략 서브타입 테이블로 전략
사용하지 말 것@Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS) - 주요 Annotation
-
@Inheritance(strategy=InheritanceType.XXX)전략 Type명 조인 전략 JOINED 단일 테이블 전략 SINGLE_TABLE 구현 클래스마다 테이블 전략 TABLE_PER_CLASS @DiscriminatorColumn(name=“DTYPE”)@DiscriminatorValue(“XXX”)
-
ex.
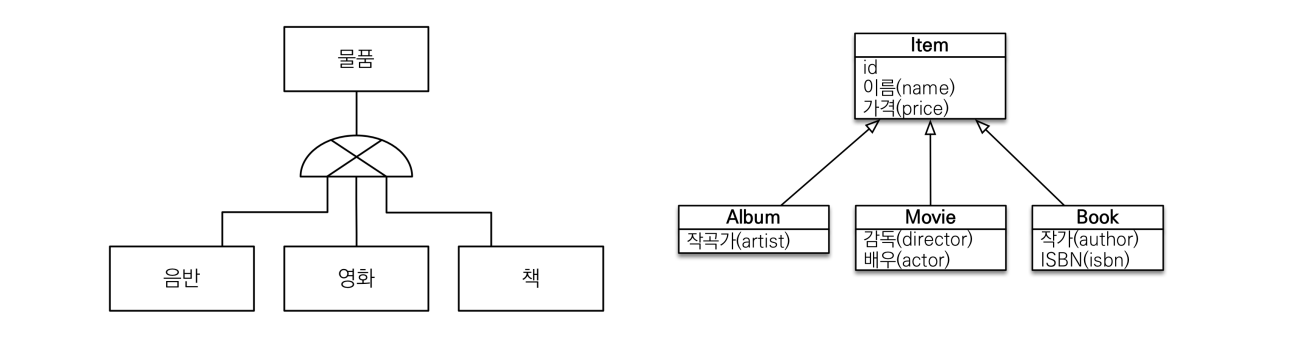
- 객체 설계시에 기본적으로 Item이라는 abstract class를 Album, Movie, Book이 상속받도록 설계
- Item만 단독으로 사용하는 경우는 없기 때문에 abstract class로 구현
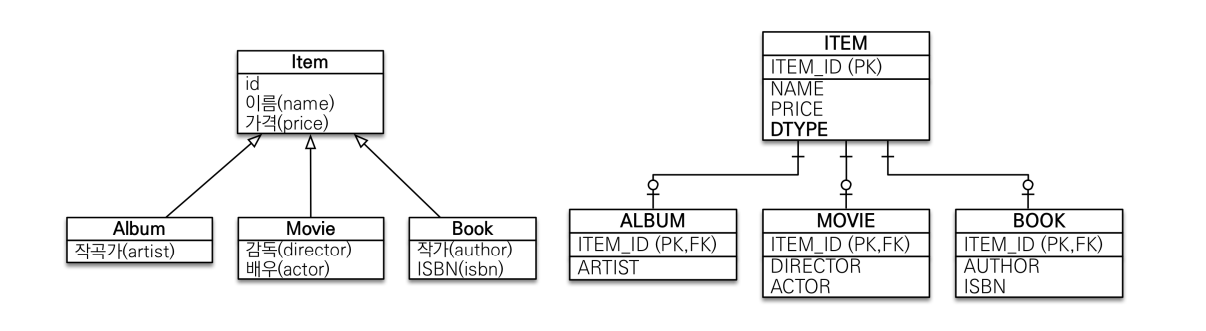
조인 전략
- 가장 권장하는 방식
- Item에
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED) -
부모 클래스에
@DiscriminatorColumn추가하여 DTYPE 추가💡
@DiscriminatorColumn- 기본적으로 하위 테이블명이 들어감
- 값을 바꿔주려면 자식 클래스에
@DiscriminatorValue("<원하는 값>") - Column명 DTYPE이 기본이지만, 변경하려면 name 이용
- 운영/DB 작업을 고려하였을 때 넣는 것을 권장
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
public class Item {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private int price;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Album extends Item {
private String artist;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Movie extends Item {
private String director;
private String actor;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Book extends Item {
private String author;
private String isbn;
// getter, setter
}
실행 결과 : Album, Book, Movie table 각각이 Item table을 참조
Hibernate:
create table Album (
artist varchar(255),
id bigint not null,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Book (
author varchar(255),
isbn varchar(255),
id bigint not null,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Item (
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255),
price integer not null,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Movie (
actor varchar(255),
director varchar(255),
id bigint not null,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
alter table Album
add constraint FKcve1ph6vw9ihye8rbk26h5jm9
foreign key (id)
references Item
Hibernate:
alter table Book
add constraint FKbwwc3a7ch631uyv1b5o9tvysi
foreign key (id)
references Item
Hibernate:
alter table Movie
add constraint FK5sq6d5agrc34ithpdfs0umo9g
foreign key (id)
references Item
Insert
// 생략
Movie movie = new Movie();
movie.setDirector("aaa");
movie.setActor("bbb");
movie.setName("바람과함꼐사라지다");
movie.setPrice(10000);
em.persist(movie);
tx.commit();
// 생략
DB
Item
| ID | NAME | PRICE |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 바람과함께사라지다 | 10000 |
Movie
| ACTOR | DIRECTOR | ID |
|---|---|---|
| bbb | aaa | 1 |
Select : Join 하여 가져옴
// 생략
Movie movie = new Movie();
movie.setDirector("aaa");
movie.setActor("bbb");
movie.setName("바람과함꼐사라지다");
movie.setPrice(10000);
em.persist(movie);
// 1차 캐시 안남도록 영속성 컨텍스트 제거
em.flush();
em.clear();
Movie findMovie = em.find(Movie.class, movie.getId());
System.out.println("findMovie = " + findMovie);
tx.commit();
// 생략
실행결과
Hibernate:
select
movie0_.id as id1_2_0_,
movie0_1_.name as name2_2_0_,
movie0_1_.price as price3_2_0_,
movie0_.actor as actor1_3_0_,
movie0_.director as director2_3_0_
from
Movie movie0_
inner join
Item movie0_1_
on movie0_.id=movie0_1_.id
where
movie0_.id=?
findMovie = hellojpa.Movie@4c7a078
- Item에 DTYPE 추가 :
@DiscriminatorColumn
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
@DiscriminatorColumn
public class Item {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private int price;
// getter, setter
}
DB
Item
| DTYPE | ID | NAME | PRICE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Movie | 1 | 바람과함께사라지다 | 10000 |
-
장/단점
구분 상세 장점 • 테이블 정규화
• 외래 키 참조 무결성 제약조건 활용가능 : ITEM_ID 활용
• 저장공간 효율화 : 정규화 되어 있으니까단점 • 조회시 조인을 많이 사용, 성능 저하
• 조회 쿼리가 복잡함
• 데이터 저장시 INSERT SQL 2번 호출
단일 테이블 전략
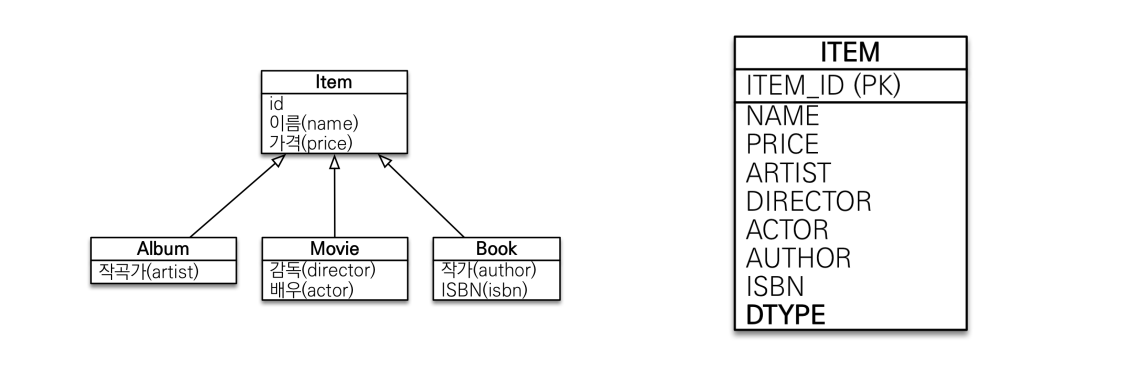
- 테이블 구분 없이 한 테이블에 모든 데이터를 넣고, DTYPE으로 구분
- Item에
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.*SINGLE_TABLE*)
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
@DiscriminatorColumn
public class Item {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private int price;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("A")
public class Album extends Item {
private String artist;
public String getArtist() {
return artist;
}
public void setArtist(String artist) {
this.artist = artist;
}
}
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("B")
public class Book extends Item {
private String author;
private String isbn;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("M")
public class Movie extends Item {
private String director;
private String actor;
// getter, setter
}
실행 결과
Hibernate:
create table Item (
DTYPE varchar(31) not null,
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255),
price integer not null,
artist varchar(255),
author varchar(255),
isbn varchar(255),
actor varchar(255),
director varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
-
@DiscriminatorColumn을 설정해주지 않아도 DTYPE 생성됨@Entity @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE) public class Item { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; private int price; // getter, setter }package hellojpa; import javax.persistence.Entity; @Entity public class Album extends Item { // 생략 }package hellojpa; import javax.persistence.Entity; @Entity public class Book extends Item { // 생략 }@Entity public class Movie extends Item { // 생략 }실행 결과
create table Item ( DTYPE varchar(31) not null, id bigint not null, name varchar(255), price integer not null, artist varchar(255), author varchar(255), isbn varchar(255), actor varchar(255), director varchar(255), primary key (id) ) - 장점
- 조인이 필요 없으므로 일반적으로 조회 성능이 빠름
-
Insert 할 때도 쿼리 한 번, 조회할 때도 Join X
Hibernate: /* insert hellojpa.Movie */ insert into Item (name, price, actor, director, DTYPE, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, 'M', ?) Hibernate: select movie0_.id as id2_0_0_, movie0_.name as name3_0_0_, movie0_.price as price4_0_0_, movie0_.actor as actor8_0_0_, movie0_.director as director9_0_0_ from Item movie0_ where movie0_.id=? and movie0_.DTYPE='M' findMovie = hellojpa.Movie@28f8e165
-
- 조회 쿼리가 단순함
- 조인이 필요 없으므로 일반적으로 조회 성능이 빠름
- 단점
- 자식 엔티티가 매핑한 컬럼은 모두 null 허용 : 데이터 무결성 관점에서 단점
- 단일 테이블에 모든 것을 저장하므로 테이블이 커지면 상황에 따라서 조회 성능이 오히려 느려질 수 있음
구현 클래스마다 테이블 전략
- 사용하지 말 것
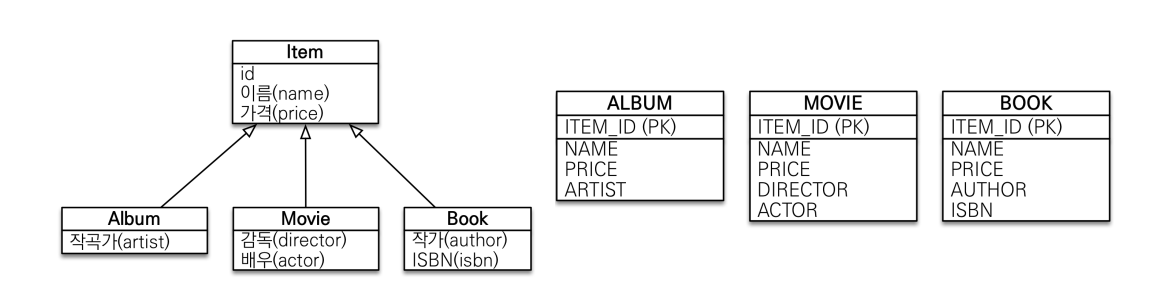
- Item table 없이 각각 테이블을 만듦 -> Name, Price Column 중복 허용
- Item에
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.*TABLE_PER_CLASS*)
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
@DiscriminatorColumn // 넣어도 의미 없음
public abstract class Item {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private int price;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Album extends Item {
private String artist;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Book extends Item {
private String author;
private String isbn;
// getter, setter
}
@Entity
public class Movie extends Item {
private String director;
private String actor;
// getter, setter
}
실행결과 : Item table이 생성되지 않음
Hibernate:
create table Album (
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255),
price integer not null,
artist varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Book (
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255),
price integer not null,
author varchar(255),
isbn varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table Movie (
id bigint not null,
name varchar(255),
price integer not null,
actor varchar(255),
director varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Insert/Select
Hibernate:
/* insert hellojpa.Movie
*/ insert
into
Movie
(name, price, actor, director, id)
values
(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
select
movie0_.id as id1_2_0_,
movie0_.name as name2_2_0_,
movie0_.price as price3_2_0_,
movie0_.actor as actor1_3_0_,
movie0_.director as director2_3_0_
from
Movie movie0_
where
movie0_.id=?
findMovie = hellojpa.Movie@589b028e
-
문제점 : 데이터를 조회할 때 부모테이블인 Item으로 조회한다면 ..?
-> union all 로 모든 테이블을 다 확인 (Insert는 괜찮음)
// 생략 Movie movie = new Movie(); movie.setDirector("aaa"); movie.setActor("bbb"); movie.setName("바람과함꼐사라지다"); movie.setPrice(10000); em.persist(movie); // 1차 캐시 안남도록 영속성 컨텍스트 제거 em.flush(); em.clear(); Item item = em.find(Item.class, movie.getId()); System.out.println("findItem = " + item); tx.commit(); // 생략Hibernate: call next value for hibernate_sequence Hibernate: /* insert hellojpa.Movie */ insert into Movie (name, price, actor, director, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?) Hibernate: select item0_.id as id1_2_0_, item0_.name as name2_2_0_, item0_.price as price3_2_0_, item0_.artist as artist1_0_0_, item0_.author as author1_1_0_, item0_.isbn as isbn2_1_0_, item0_.actor as actor1_3_0_, item0_.director as director2_3_0_, item0_.clazz_ as clazz_0_ from ( select id, name, price, artist, null as author, null as isbn, null as actor, null as director, 1 as clazz_ from Album union all select id, name, price, null as artist, author, isbn, null as actor, null as director, 2 as clazz_ from Book union all select id, name, price, null as artist, null as author, null as isbn, actor, director, 3 as clazz_ from Movie ) item0_ where item0_.id=? findItem = hellojpa.Movie@53cdecf6 -
장/단점
구분 상세 장점 • 서브 타입을 명확하게 구분해서 처리할 때 효과적
• not null 제약조건 사용 가능 : 테이블을 따로 생성하였으므로단점 • 여러 자식 테이블을 함께 조회할 때 성능이 느림(UNION SQL 필요)
• 자식 테이블을 통합해서 쿼리하기 어려움
• 변경할 때 많은 것을 수정해야 함
2. @MappedSuperclass
@MappedSuperclass
-
공통 매핑 정보가 필요할 때 사용(id, name)
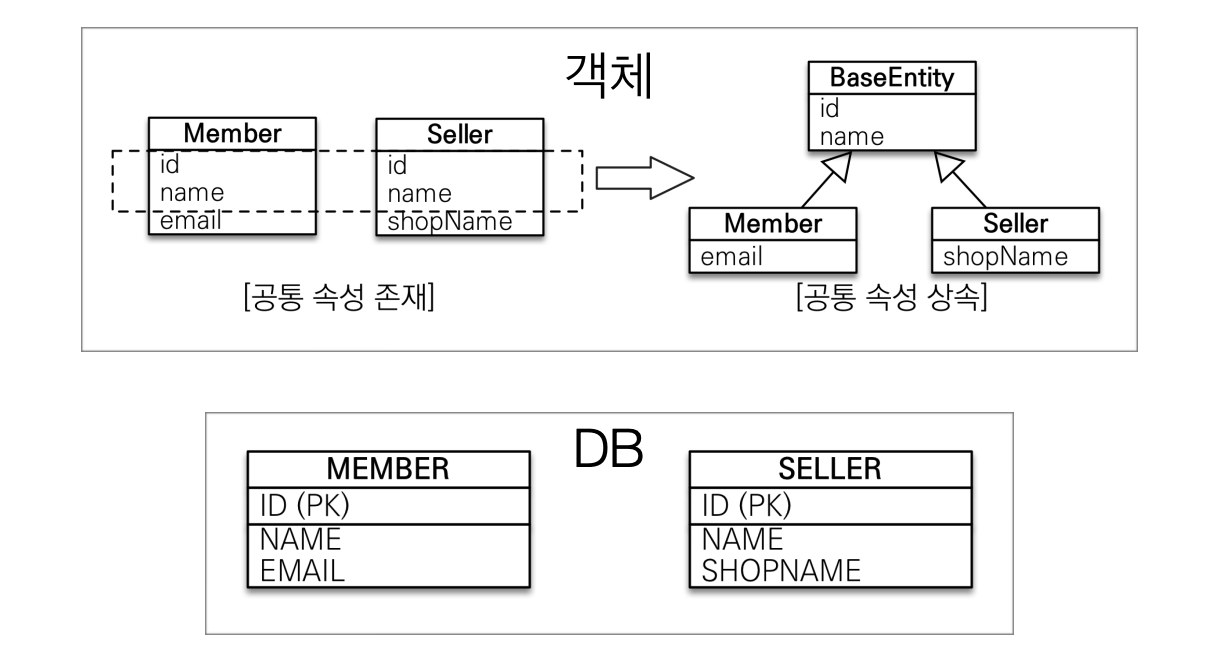
- 사용 방법
- 공통 속성을 담은 추상 클래스를 만들고
@MappedSuperclassAnnotation - 공통 속성이 포함된 클래스는 공통 속성을 상속받음(extends)
- 공통 속성을 담은 추상 클래스를 만들고
- 예제
- BaseEntity.java가 공통 속성을 담고 있고, Member, Team이 이 공통 속성을 포함함
-
BaseEntity.java : 공통 매핑 정보 담음
@MappedSuperclass public abstract class BaseEntity { @Column(name = "INSERT_MEMBER") private String createdBy; private LocalDateTime createdDate; @Column(name = "UPDATE_MEMBER") private String lastModifiedBy; private LocalDateTime lastModifiedDate; // getter, setter 생략 }Member.java
@Entity public class Member extends BaseEntity { @Id @GeneratedValue @Column(name = "MEMBER_ID") private Long id; @Column(name = "USERNAME") private String username; @ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name = "TEAM_ID", insertable = false, updatable = false) // 매핑은 되어있는데 읽기 전용 !!!! private Team team; @OneToOne @JoinColumn(name = "LOCKER_ID") // 이걸 넣지 않으면 자동으로 값이 들어가는데, 직관적이지 않음 private Locker locker; @OneToMany(mappedBy = "member") private List<MemberProduct> memberProducts = new ArrayList<>(); // getter, setter 생략 }Team.java
@Entity public class Team extends BaseEntity { @Id @GeneratedValue @Column(name = "TEAM_ID") private Long id; private String name; @OneToMany @JoinColumn(name = "TEAM_ID") private List<Member> members = new ArrayList<>(); // getter, setter 생략 }
- 특징
- 상속관계 매핑 X
- 엔티티 X. 따라서 테이블과 매핑 X
- BaseEntity 테이블은 만들어지지 않음
- 부모 클래스를 상속 받는 자식 클래스에 매핑 정보만 제공
- 조회, 검색 불가 ex. em.find(BaseEntity) 불가
- 직접 생성해서 사용 X -> 추상 클래스 권장
- 테이블과 관계 없고, 단순히 엔티티가 공통으로 사용하는 매핑 정보를 모으는 역할
- 주로 등록일, 수정일, 등록자, 수정자 같은 전체 엔티티에서 공통으로 적용하는 정보를 모을 때 사용
- 참고:
@Entity클래스는 엔티티나@MappedSuperclass로 지정한 클래스만 상속 가능@Entity: 상속 관계 매핑@MappedSuperclass: 속성만 상속 받을 때

Leave a comment